If you’ve ever tuned into the hit TV show “How It’s Made”, you’re probably the type of person who enjoys understanding all of the components and processes that make up your favorite products. When it comes to CBD, many people are just as curious about its origins, leading many to ask the same questions about their favorite cannabinoid: “How is CBD made?”.
The answer to ‘how to make CBD’ is probably a lot more simple than you realize: grow a plant, extract the cannabinoids & terpenes, isolate the ones you’re seeking, and put them into your desired delivery method.
See? As simple as baking a cake if you first had to grow your own ingredients, clean & process them to your desired substance and somehow whip them into an edible batter…
All jokes aside, learning how to extract CBD from cannabis or CBD extraction from hemp are the most technical and difficult steps of the entire procedure. There are several methods to learn how CBD is extracted, but modern advances in technology have made doing so very efficient and precise. Nowadays, extraction experts can isolate specific molecules such as CBD, Limonene or any other cannabinoid/terpene and optimize how effectively they are extracted.

Today is a golden age for cannabinoid extraction, which is one of the reasons why there are so many innovative CBD products hitting the shelves, seemingly each week. Shopping for high-potency CBD, THC or other cannabinoid products has never been easier – especially if you’re looking online for whatever cannabinoid scratches your particular itch.
Although certain conventional medicine experts would have you believe that CBD is derived from some hokey, quasi-shamanistic procedures, there’s no questioning how beneficial Cannabidiol can be.
CBD is making a difference in the lives of a growing number of people, and with modern technology & expertise the sky’s the limit for what kinds of products can be made with hemp Cannabidiol.
What kinds of equipment, procedures and know-how are essential for CBD extraction from hemp? What is CBD oil made from? Is it difficult to learn the CBD extraction process? Let’s take off our gardening gloves and trade them in for a lab-coat as we learn how to extract CBD.
WHAT IS CBD OIL MADE FROM?
Before we understand how it’s made, we need to go over what is made when we’re talking about CBD from hemp. CBD is just one of hundreds of known phytocannabinoids found in cannabis and hemp. Cannabinoids like CBD, THC, CBN and CBG are the active compounds that are produced by Cannabis sativa L., Cannabis indica Lam., and Cannabis ruderalis – all members within the Cannabaceae family.
Cannabidiol has grown to prominence in the medical & nutritional worlds because it is distinctly non-psychoactive, whereas its cannabinoid-cousin THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) is primarily responsible for the “high” people associate with consuming cannabis. For these reasons, hemp CBD has become the cannabinoid of choice for millions of people around the globe.
CBD extraction from hemp has skyrocketed in popularity & technological sophistication, which has led to a number of innovative products that contain Cannabidiol in all its forms. What are these different forms? There are three major categories of CBD that can be extracted from both hemp and cannabis plants:

CBD Isolate
Like its name suggests, CBD isolate is a type of Cannabidiol that is extracted on its own from the rest of the spectrum of cannabinoids. By isolating CBD, you can be assured that you’re getting CBD in one of its purest forms, and that there is zero-THC in the final product.
Isolated Cannabidiol is definitely one of the more popular types of CBD on the market, and with modern extraction techniques (we’ll get into these later on in the article) extractors are capable of isolating 99%+ pure Cannabidiol!
Broad Spectrum CBD
One step up from isolates is Broad Spectrum CBD. This form of Cannabidiol does include other terpenes & cannabinoids from the plant (cannabis/hemp), but in the final processing steps THC is typically removed from the finished product.
Why is THC so reviled? Well we covered the fact that THC is the primary psychoactive agent for the mind-altering effects of cannabis, but it’s absence is also a legal requirement in places like the United States. According to the Farm Bill, passed in December 2018 at the Federal level, any CBD product must contain less than 0.3% THC.
Keep in mind that certain States have ratified both cannabis and hemp products – and all their derivative cannabinoids & terpenes – so this <0.3% THC ruling applies to hemp CBD products specifically, at the federal level.
Full-Spectrum CBD
Similar to CBD Isolate, Full-Spectrum CBD is quite obvious when you consider its name. This form of Cannabidiol includes the full gamut of terpenes, flavonoids and cannabinoids from any given plant. Yes, that does include THC. If these kinds of products contain CBD, how are they legal?!
As we mentioned, certain States have legalized medical, recreational cannabis & hemp, which allows them to sell products from both plants with the full spectrum of cannabinoids. We’ve included a helpful snapshot of the legal cannabis U.S. States for your reference, but keep in mind the landscape for legal cannabis and others is constantly shifting.
Hemp Full-Spectrum CBD products do contain trace amounts of THC and other cannabinoids, but one of hemp’s major advantages over cannabis is the fact that it contains far lower Tetrahydrocannabinol contents on average.
Therefore, a hemp Full-Spectrum product might include a small percentage of THC, but CBD can work to counterbalance the psychoactive effects of THC if they’re taken together. Add to this the host of entourage effects from combining cannabinoids together, and it’s easy to see why Full-Spectrum products are growing in popularity across the United States.
We will answer the question ‘how is CBD extracted’ in the next section of this article, but first let’s quickly analyze what ingredients are typically involved in making CBD products. Once hemp or cannabis plants have been harvested and processed, there are a few components needed in order to house your newly extracted Cannabidiol. The essential components of any CBD product are:

Base/Carrier
Depending on what kind of CBD product we’re discussing, CBD needs to be contained in a carrier agent – such as MCT or hemp oil base for tinctures, inert creams or gels for topicals, and water-based liquid for sprays & edibles.
CBD Extract
We’ll learn how to extract CBD oil from cannabis and hemp later on, but this is the heart-and-soul of the CBD product in question. How concentrated your Cannabidiol is, how pure it might be, and what form you prefer (isolate powder, full-spectrum oil, broad spectrum resin, etc) are determined by your extraction methods and how potent of a product you are seeking to manufacture.
For instance, a medical-grade CBD salve for severe burns or chronic eczema will most likely contain the entire cannabinoid & terpene profile of the plant for the combined CBD benefits of the entourage effect (Full-Spectrum) in a neutral gel or liquid base of other nourishing ingredients like Aloe Vera. In another example, a CBD oil tincture that is meant to be taken as a daily health supplement will contain CBD isolate in an MCT, olive, or hemp oil base.
The CBD extraction process will determine the overall potency of the final CBD product, which will in-turn narrow the manufacturers’ options for product-type. That being said, there are no standards for dosing or CBD strength, as you will notice whenever you shop for CBD online – Cannabidiol concentrations vary greatly from one brand to another. The important thing is that there are many choices and customization options for dosing Cannabidiol, as each person has unique health needs & wants.
Delivery System
How you deliver CBD to your system is wholly a matter of choice, but certain product types offer greater flexibility or customization than others. For example, CBD oils typically contain the highest potency CBD: 500 mg – 5000 mg, on average. Therefore, CBD oil is one of the more prominent delivery methods on the market today – not only because they offer high-doses that can be calculated precisely with each drop/dropper, but also because CBD oil can be ingested orally or applied topically.
Other products can house higher doses of CBD if need-be, however CBD oil still maintains its advantages due to the fast-efficient absorption of Cannabidiol through your sublingual glands under your tongue. This is considered by many studies to be one of the most effective ways to deliver CBD to your system. Simply by taking your required dose under the tongue and holding it there for 15-30 seconds, your sublingual glands are able to absorb the Cannabidiol content more efficiently. This is due to the fact that sublingual absorption bypasses your digestive system and metabolization in the liver for direct access to your Endocannabinoid System (ECS).
This is not to suggest that other CBD products are inferior delivery methods, quite the contrary in fact. How you introduce CBD into your body is completely up to you, and certain products will be more efficient, effective and most of all convenient for you. Many people prefer gummies because they taste great, others like the oral spray for its easy one-pump system, while other consumers choose CBD creams because they provide targeted relief to sore or irritated areas.
How you choose to deliver CBD to your system is not the primary concern – it’s all about personal preferences and what fits your lifestyle/needs the best. It is definitely recommended that you experiment with different product types and variable doses, in order to determine the best possible CBD routine for optimum benefits to your health & wellness.

Complimentary/Beneficial Ingredients
Any beneficial ingredients that you might find in vitamins, supplements or natural remedies at your local retailer could fit into this section. Natural inputs like melatonin, B vitamins, MSM, aloe vera, arnica, ashwagandha root extract and a number of beneficial, herbal ingredients like lavender & chamomile are commonly found alongside hemp CBD.
The ingredient profile of a given CBD product will likely be formulated based on its intended use(s) – boosting immunity, providing mental calm, improving sleep quality or invigorating your body & mind. In most cases, Cannabidiol is meant to be the primary active ingredient, but it is important to select products that also offer a wide range of beneficial macro & micro nutrients as well.
Flavor/Aroma Additives
Flavorings are best when they’re naturally derived, but there are also many people who prefer no flavor/aroma additives at all. These kinds of ingredients are typically added to mask the tastes & smells of hemp – some people do not enjoy the slightly nutty, semi-herbal taste – and yet there are many more who do like the sensations of hemp or cannabis.
Flavors and aromas like citrus, mint, pine, berry, chocolate and cinnamon are very common in CBD products today, but there really is no limit to the kinds of tastes, textures and scents of any given product. As we mentioned just before, the dominant trend for CBD products today is to have neutral, flavor- and fragrance-free products because many people have allergies or aversions to particular additives.
HOW TO EXTRACT CBD
There are several CBD extraction processes used today, some that are doable at home while others require a lot more technical equipment, training & knowhow. Once you’ve grown your preferred genetics, harvested and processed the flower & relevant plant material, you’re ready to get down to the nitty-gritty and extract the goods.
Because learning how CBD is made involves a lot of steps already, we’ll do our best to summarize these complicated extraction processes into easy-to-understand, simple steps. Not everyone is interested in extracting CBD from their own plants at home, but there are methods you can employ with simple household set-ups, so we’ll cover these in addition to the professional extraction techniques.
There are roughly 4 major extraction techniques that are used across the globe today: CO2 Extraction, Dry Ice Extraction, Solvent Extraction and Oil Extraction.
#1 CO2 Extraction
ADVANTAGES: Safe, commonly used for food extractions/processing, does not compromise essential oils (terpenes, cannabinoids) during extraction, maintains high-purity & consistency of active compounds
DISADVANTAGES: requires expensive & technical equipment, training & professional knowledge of safe operation is essential
CO2 extraction is the most widely used extraction method for obtaining safe, high-potency cannabinoids like CBD, THC, CBN and others without introducing any potentially harmful chemicals. There are three subtypes of CO2 extraction – supercritical, subcritical and mid-critical – but supercritical is usually the only method used because it yields the most pure & high-potency extracts.
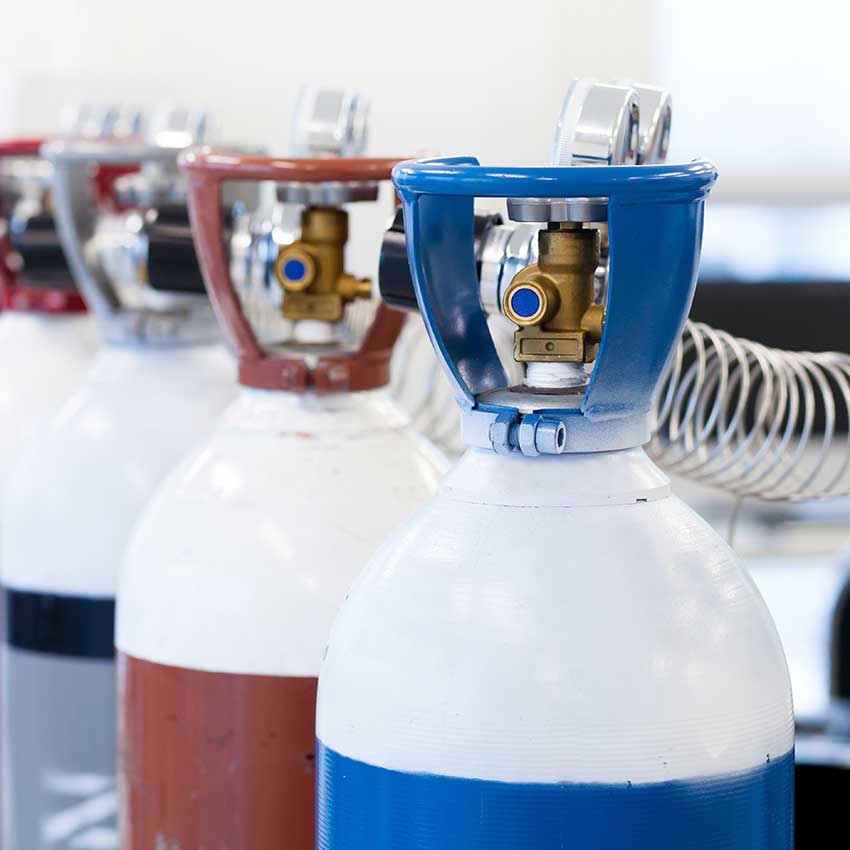

To extract CBD from hemp or cannabis, the CO2 needs to be dropped in temperature and pressurized (-69℉ and 75 lbs psi) for it to become “supercritical” – i.e. the state between gas and liquid where CO2 can permeate the air like a gas but still remaining dense enough to extract terpenes and cannabinoids from the plant.
When CO2 is in this supercritical state, it can be applied to cannabis or hemp flowers and in effect pulls the active compounds from the plant. The CO2 is then passed through a separator/containing chamber where the terpenes & cannabinoids are captured while the supercritical CO2 is collected into a condenser and returned to its original state. This allows the extractor to use the CO2 all over again, creating an efficient, sustainable and closed-loop system for extraction.

#2 Dry Ice Extraction
ADVANTAGES: Easy to learn, not much equipment/knowledge required, easy cleanup, average extraction yields are higher than oil extraction methods
DISADVANTAGES: user-error is common, can negatively impact extraction purity/quality, dry ice is not always cheap/easy-to-obtain, dangers of dry ice burns & intoxication
Dry ice extraction is a much more simple – but not as efficient – method of extracting cannabinoids. Simply put, you place cannabis/hemp flowers in a container with dry ice and allow the trichomes to freeze to the point of breaking off. Then, by disturbing the flowers (shaking, vibrating, etc) over different layers of micron sieves, filters or bags, you can capture the frozen trichomes as they break off from the buds.
#3 Solvent Extraction
ADVANTAGES: Not technically complicated, does not involve much set-up or equipment, can be very efficient for extracting high-quality oils
DISADVANTAGES: Risks of flammable materials (butane, ethanol), can breakdown essential waxes/oils of the plant, can leave residual compounds in the finished product
Solvent extraction can be tricky as the legality of using organic/inorganic solvents can vary between countries, states and provinces. This is because of the potential for residual chemicals and contaminants in the extracted products, such as chlorophyll and other other organic compounds that can irritate/harm the lungs when ingested.

To avoid these contaminants being present in the extraction, additional filtering stages can be employed but these extra steps will also lower the purity/potency of the cannabinoids & terpenes.
Nonetheless, solvent extraction such as methods that utilize butane, ethanol or alcohol are very commonplace in smaller cannabis/hemp outfits. In these cases, solvents are applied to the plant materials whereby the solvents strip cannabinoids/terpenes, which are then heated to separate the phytocompounds from the solvent in the form of natural oils.

#4 Oil Extraction
ADVANTAGES: Very safe, easy to do at home, user-friendly, cost-effective
DISADVANTAGES: Not as stable shelf-life of finished product, typically much lower yields of cannabinoid/terpene potency with this method, involves additional decarboxylation steps
Oil extraction usually involves olive oil, hemp seed oil or coconut oil, but it is really up to the extractor to choose which base/carrier agent they use. Oil extraction is the most common method used at home, and for good reason – all you need is some very cost-friendly oil, an oven, stovetop and everyday household containers/utensils.
First, you need to decarboxylate the flowers in the oven – Decarboxylation is the process whereby heat is applied to the buds and chemically alters the cannabinoids from their raw, acidic forms (THCA, CBDA, CBGA, etc) into the active compounds we’re seeking (THC, CBD). Once you’ve decarbed your flowers, simply add the ‘cooked’ buds to a pot of oil and heat it on high (200-215℉) for 1-2 hours.
The terpenes, cannabinoids and essential plant oils will separate into the oil mixture, allowing you to filter the plant material out and being left with CBD-infused DIY oil. Most people who do their own oil extractions will then use their homemade CBD oil in edibles, teas, or topicals.
Before you ever attempt your own extractions, it is imperative that you have all the relevant safety equipment, PPE, and training. There are numerous health risks to yourself and others if you do not perform the necessary checks & balances when using supercritical gases, solvents or substances like dry ice.
Just like when you’re dosing with new cannabinoids or strains of cannabis/hemp for the first time, be sure to start low and go slow through the processes of making your own CBD products. Even if you’re not keen on creating your own CBD extracts, it is valuable to understand ‘how is CBD made’ in order to shop for the product that best suits your needs. There are as many ways to make CBD products as there are cannabinoids & terpenes in the plant.
If you do your research on the CBD products & services before you buy, you’ll avoid some of the bad CBD experiences in favor of the truly beneficial ones.
FAQ’s
How is CBD produced?
Cannabidiol (CBD) is typically extracted from the hemp plant – specifically the flowers or “buds”, leaves and stem, but whole-plant extraction is also a commonly used method. Once extracted, CBD is included in many kinds of products, such as topicals, oils, edibles and other ingestible forms such as vapes.
Where does CBD come from?
CBD – Cannabidiol – is a cannabinoid found in cannabis & hemp, along with hundreds of other active compounds such as THC, CBN, CBG, etc. CBD is most commonly extracted using CO2, Ethanol or other organic solvents.
What part of the plant does CBD come from?
CBD in cannabis is most prominently concentrated in the flowers/buds, but when extracted from hemp typically the ‘whole plant extraction’ method includes isolating this valuable cannabinoid from the flowers, leaves and stems. Only the roots & seeds are typically not used for extracting Cannabidiol. To be precise, cannabinoids and terpenes reside in the plant’s resin – the waxy or sap-like secretions that are produced by the hemp plant as part of self-defense/reproduction.
Can I drive after taking CBD oil?
CBD is typically safe to consume as they have no psychoactive effects – mind-altering influences or associated “high” – but be mindful that some CBD products may contain other cannabinoids, such as THC. To be on the safe side, never drive a vehicle or operate machinery unless you are very familiar with the CBD source in question and you understand its effects on your mind & body.
Can CBD cause gas?
Cannabidiol is not typically associated with causing gas or bloating – in fact, its anti-inflammatory properties make it quite proficient for reducing the symptoms of nausea, indigestion or irritated bowels. Nonetheless, some people have reported that CBD ingestion caused them some discomfort, but these cases have been few and far between.









